In this tutorial, we will create a Flutter app to find the LCM of two numbers. This app will help you understand form validation, input handling, and UI updates in Flutter.
Table of Contents

Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Setting Up the Flutter app to find the LCM
Before we start, make sure you have Flutter installed. Follow the official Flutter installation guide if you haven’t done so already.
Create a new Flutter project by running the following command in your terminal:
flutter create lcm_calculator
cd lcm_calculator
Open the project in your preferred code editor.
Step 2: Writing the Flutter app to find the LCM
First, we’ll define the main entry point of our Flutter application. Replace the content lib/main.dart with the following code:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'LCM Calculator',
home: LCMCalculatorScreen(),
);
}
}
Here, we define a MyApp class that extends StatelessWidget. This class builds a MaterialApp with the title ‘LCM Calculator’ and sets LCMCalculatorScreen it as the home screen.
Step 3: Creating the Flutter app to find the LCM
Next, we’ll create the main screen for our app. Add the following code to lib/main.dart:
class LCMCalculatorScreen extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_LCMCalculatorScreenState createState() => _LCMCalculatorScreenState();
}
class _LCMCalculatorScreenState extends State<LCMCalculatorScreen> {
final _formKey = GlobalKey<FormState>();
final _num1Controller = TextEditingController();
final _num2Controller = TextEditingController();
int _lcmResult = 0;
int _findLCM(int a, int b) {
int maxNum = a > b ? a : b;
while (true) {
if (maxNum % a == 0 && maxNum % b == 0) {
return maxNum;
}
maxNum++;
}
}
void _calculateLCM() {
if (_formKey.currentState!.validate()) {
setState(() {
int num1 = int.parse(_num1Controller.text);
int num2 = int.parse(_num2Controller.text);
_lcmResult = _findLCM(num1, num2);
});
}
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('LCM Calculator'),
),
body: Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(20.0),
child: Form(
key: _formKey,
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
TextFormField(
controller: _num1Controller,
keyboardType: TextInputType.number,
decoration: InputDecoration(
labelText: 'Enter first number',
),
validator: (value) {
if (value == null || value.isEmpty) {
return 'Please enter a number';
}
return null;
},
),
SizedBox(height: 20),
TextFormField(
controller: _num2Controller,
keyboardType: TextInputType.number,
decoration: InputDecoration(
labelText: 'Enter second number',
),
validator: (value) {
if (value == null || value.isEmpty) {
return 'Please enter a number';
}
return null;
},
),
SizedBox(height: 20),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _calculateLCM,
child: Text('Calculate LCM'),
),
SizedBox(height: 20),
Text(
'LCM: $_lcmResult',
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 20),
),
],
),
),
),
);
}
}
In this code:
- Inside
_LCMCalculatorScreenState, we create controllers for the input fields and a form key for validation. - The
_findLCMmethod calculates the LCM of two numbers using an iterative approach. - The
_calculateLCMmethod validates the input, parses the numbers, and calculates the LCM. - The
buildmethod constructs the UI, includingTextFormFieldwidgets for input, aElevatedButtonto trigger the calculation, and aTextwidget to display the result.
Step 4: Running the App
You can now run your app using the following command:
flutter run
Full code:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'LCM Calculator',
home: LCMCalculatorScreen(),
);
}
}
class LCMCalculatorScreen extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_LCMCalculatorScreenState createState() => _LCMCalculatorScreenState();
}
class _LCMCalculatorScreenState extends State {
final _formKey = GlobalKey<FormState>();
final _num1Controller = TextEditingController();
final _num2Controller = TextEditingController();
int _lcmResult = 0;
int _findLCM(int a, int b) {
int maxNum = a > b ? a : b;
while (true) {
if (maxNum % a == 0 && maxNum % b == 0) {
return maxNum;
}
maxNum++;
}
}
void _calculateLCM() {
if (_formKey.currentState!.validate()) {
setState(() {
int num1 = int.parse(_num1Controller.text);
int num2 = int.parse(_num2Controller.text);
_lcmResult = _findLCM(num1, num2);
});
}
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('LCM Calculator'),
),
body: Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(20.0),
child: Form(
key: _formKey,
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
TextFormField(
controller: _num1Controller,
keyboardType: TextInputType.number,
decoration: InputDecoration(
labelText: 'Enter first number',
),
validator: (value) {
if (value == null || value.isEmpty) {
return 'Please enter a number';
}
return null;
},
),
SizedBox(height: 20),
TextFormField(
controller: _num2Controller,
keyboardType: TextInputType.number,
decoration: InputDecoration(
labelText: 'Enter second number',
),
validator: (value) {
if (value == null || value.isEmpty) {
return 'Please enter a number';
}
return null;
},
),
SizedBox(height: 20),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _calculateLCM,
child: Text('Calculate LCM'),
),
SizedBox(height: 20),
Text(
'LCM: $_lcmResult',
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 20),
),
],
),
),
),
);
}
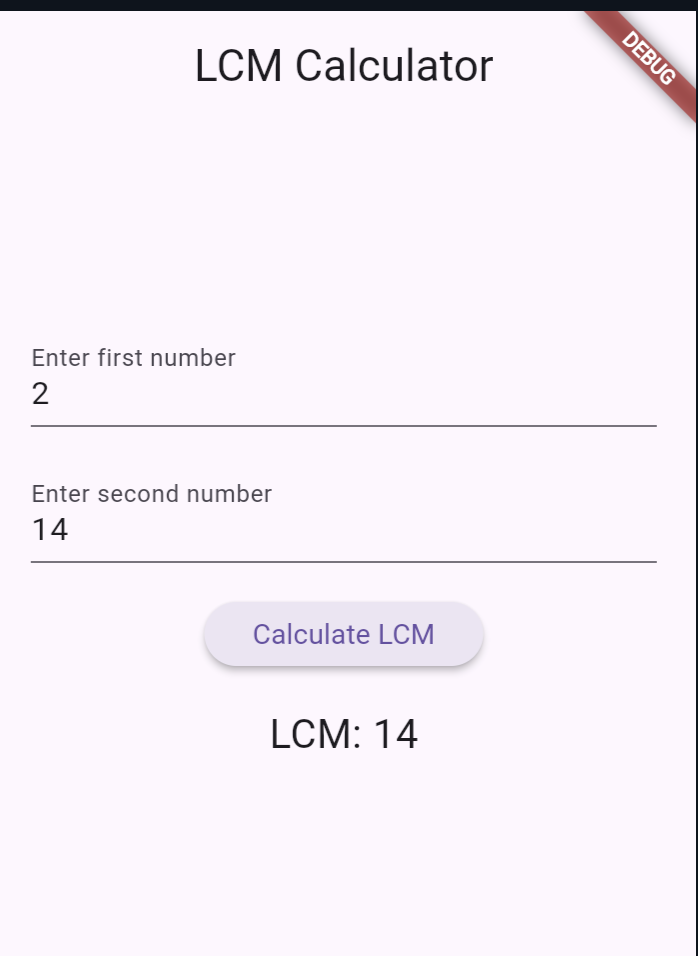
}This will launch the app in the emulator or on a connected device. Enter two numbers in the input fields, tap the “Calculate LCM” button, and you’ll see the LCM displayed below.
Output:
Also read:
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we built a simple Flutter app to calculate the LCM of two numbers. We covered form validation, handling input, and updating the UI dynamically. This tutorial provides a foundation for building more complex mathematical and utility apps in Flutter.
